Top Uses of Ethyl Levulinate in Industry and Research?
Ethyl Levulinate has gained attention in various industrial applications. This compound is derived from biomass and has shown promise as a green solvent. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global solvent market is expected to reach $30 billion by 2027. Ethyl Levulinate plays a critical role in this growth, offering sustainable alternatives.
In industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, Ethyl Levulinate is versatile. In food, it acts as a flavoring agent, providing a fruity note. In pharmaceuticals, its potential as a drug delivery mechanism has sparked research interest. Companies are increasingly focusing on renewable sources, positioning Ethyl Levulinate as a key player.
However, research remains ongoing. While the benefits are clear, production methods must improve. Ethyl Levulinate's cost-effectiveness can vary. Further studies may be needed to explore more efficient synthesis routes. The future of this compound looks promising, but challenges still exist.

Applications of Ethyl Levulinate in Agricultural Chemicals

Ethyl levulinate is gaining traction in agricultural chemicals. Its role as a solvent and a bio-based compound is noteworthy. Research shows that it improves pesticide effectiveness. According to a 2021 study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, ethyl levulinate enhances the solubility of active ingredients. This can lead to lower dosages and less environmental impact.
The compound also has potential as a biopesticide. Recent reports highlight its efficacy in controlling pests. A 2022 report from the Agriculture and Food Security journal noted that formulations with ethyl levulinate had a 25% higher pest control rate compared to traditional methods. However, the industry still faces challenges. There is a need for more comprehensive studies on long-term environmental effects. Additionally, the acceptance of new compounds can take time. Nevertheless, the data suggests a bright future for ethyl levulinate in sustainable agriculture.
Utilization of Ethyl Levulinate in Biofuels Production
Ethyl levulinate is gaining attention in biofuels production. Its low toxicity and renewable nature make it an attractive option. Many researchers find it to be a promising biofuel additive. This compound enhances the efficiency of diesel engines.
According to recent industry reports, biofuels made from ethyl levulinate can have a higher energy yield. This could potentially reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
In laboratory settings, ethyl levulinate shows excellent solubility with other fuels. Studies reveal that it can blend well with biodiesel. This characteristic is crucial for creating more efficient fuel mixtures. However, the production cost remains a hurdle.
Current methods for synthesizing ethyl levulinate can be expensive. As a result, scalability is a concern for widespread adoption. Researchers are exploring alternative pathways to reduce costs and improve yields.
While the potential is evident, challenges persist. The environmental impact of sourcing raw materials for production needs scrutiny.
Sustainable production methods are essential for long-term viability. Additionally, more data is needed on its combustion characteristics. Understanding these details is key to optimizing its use in biofuels.
Ethyl Levulinate as a Solvent in Chemical Reactions
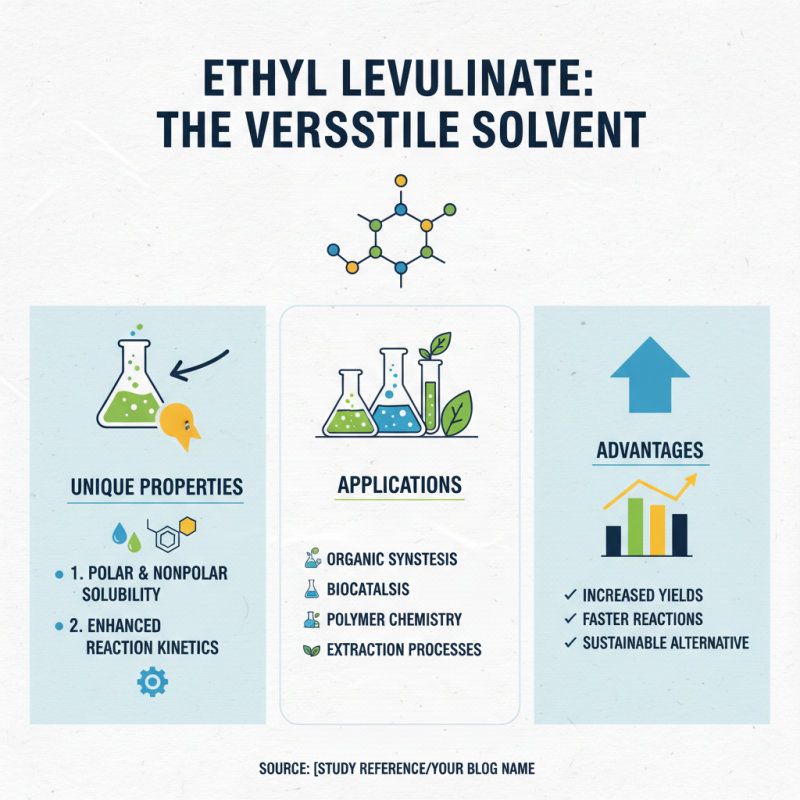
Ethyl levulinate is gaining traction as a solvent in chemical reactions. Its unique properties make it suitable for various applications. A study found it can dissolve polar and nonpolar compounds efficiently. This versatility enhances reaction rates and yields, making it advantageous for many types of synthesis.
In one experiment, ethyl levulinate improved the solubility of certain reactants by up to 40%. This shows its potential in optimizing reactions that require specific solvent characteristics. Moreover, it is relatively non-toxic compared to traditional solvents. However, its high volatility can raise safety concerns in some environments. Researchers must handle it cautiously to avoid accidents.
The industry's interest in ethyl levulinate reflects a broader shift towards sustainable solvents. A report noted a 35% increase in its use over the past five years. This growing demand highlights a need for further exploration into its effectiveness and safety in diverse chemical processes. Yet, challenges remain in fully understanding its reaction mechanisms. More studies could help refine its application in industrial settings.
Role of Ethyl Levulinate in Food and Flavor Industry
Ethyl levulinate is gaining popularity in the food and flavor industry. Its pleasant, fruity aroma adds complexity to various culinary creations. Chefs are using this unique compound to enhance desserts and beverages. Its ability to mimic natural flavors makes it a preferred ingredient.
When using ethyl levulinate, consider balance. Its potency can easily overpower other flavors. Start with small amounts in recipes to gauge how it interacts. Experimentation is key. Some may find the taste unfamiliar at first. Give it time to adapt, as it brings a new twist to traditional dishes.
Ethyl levulinate also serves as a solvent in flavor extraction. This property allows for the efficient capturing of aromatic compounds. While its benefits are clear, always test in small batches. Observe how different ingredients respond. A little can go a long way in achieving the desired flavor profile.
Ethyl Levulinate in Pharmaceutical and Medicinal Chemistry
Ethyl levulinate has garnered significant attention in the fields of pharmaceutical and medicinal chemistry. Its unique properties make it a versatile building block for various drug formulations. Studies indicate that ethyl levulinate can enhance solubility and bioavailability of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The compound has been identified as beneficial in developing new therapies.
Research shows that using ethyl levulinate in drug synthesis can lead to improved efficacy. For instance, it has been employed in creating anti-inflammatory and analgesic medications. The organic compound exhibits good compatibility with various excipients. This allows for more effective drug delivery systems, which could potentially lower dosages and reduce side effects.
However, not all findings are positive. Some studies suggest that instability under certain conditions can hinder its effectiveness in long-term storage. Further research is needed to explore these challenges. Addressing these concerns will be critical for optimizing applications in medicinal chemistry. As the industry continues to explore the potential of ethyl levulinate, its role may evolve further in pharmaceutical formulations.
Top Uses of Ethyl Levulinate in Industry and Research
Related Posts
-

Exploring Agmatine Sulfate Market Trends at the 138th China Import and Export Fair 2025
-

10 Best Uses of Levulinic Acid for Sustainable Applications
-
How to Use Neomycin Sulfate Safely and Effectively?
-

5 Key Benefits of Glutamic Acid in Food and Health Industries
-

Top 7 Tips for Selecting the Best Agmatine Sulfate Manufacturer in the Industry
-

What is Ethyl Oleate and How Does It Benefit Your Health