What is Glutamic Acid and Why is it Important?
Glutamic Acid is a vital amino acid found in many foods such as meat, fish, and dairy. It plays a key role in protein synthesis and neurotransmitter functions. According to the Journal of Nutrition, around 25% of the amino acids in the human body consist of glutamic species. This highlights its importance in maintaining overall health.
In the food industry, glutamic acid is widely utilized as a flavor enhancer. The use of monosodium glutamate (MSG), derived from glutamic acid, has been a point of discussion. Some studies, including those by the FDA, suggest that MSG can enhance umami flavor without significant adverse effects. Yet, some individuals report sensitivity, prompting ongoing research and debate.
Despite its many benefits, the industrial production of glutamic acid raises concerns. Environmental impact and ethical production methods are areas needing examination. As the demand for glutamic acid grows, it challenges industry practices. Balancing health benefits with environmental responsibilities is crucial for future production.

Definition and Chemical Structure of Glutamic Acid
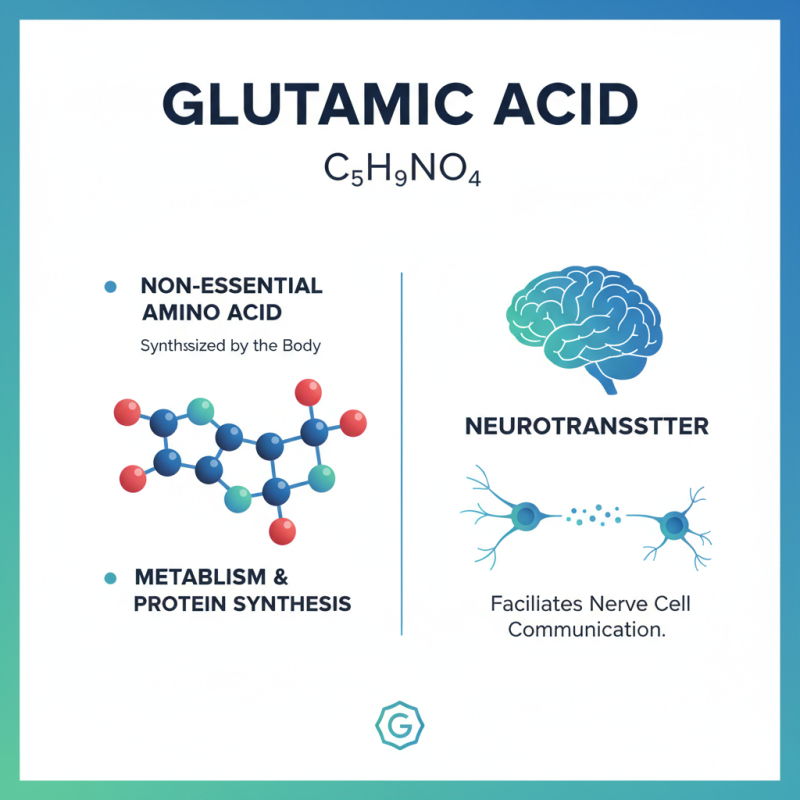
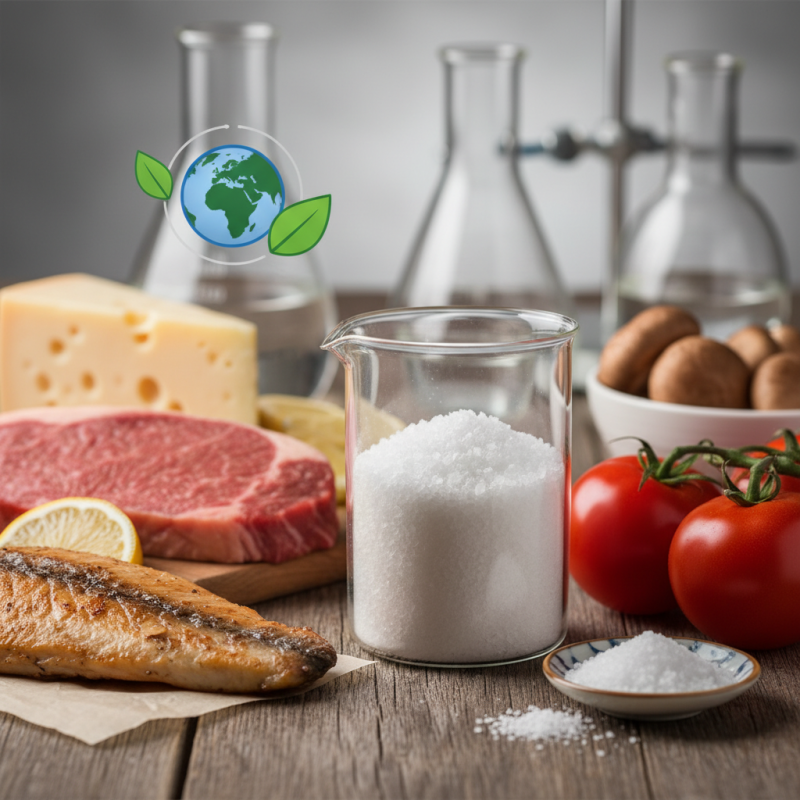
Glutamic acid is an amino acid with the chemical formula C5H9NO4. It is classified as a non-essential amino acid. This means our body can synthesize it. Glutamic acid is crucial in metabolism and protein synthesis. It often serves as a neurotransmitter in the brain, facilitating communication between nerve cells.
Structurally, glutamic acid features a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a side chain that distinguishes it from other amino acids. The side chain contains a second carboxyl group. This unique structure allows glutamic acid to participate in various biochemical processes. According to a report by the National Institutes of Health, glutamic acid plays a significant role in cognitive function. It helps in memory and learning by supporting synaptic plasticity.
With over 80% of the brain's neurotransmitter activity influenced by glutamic acid, its importance cannot be overstated. Yet, an excess of this amino acid can lead to negative effects. High levels may contribute to neural excitotoxicity, a phenomenon that can damage nerve cells. Balancing glutamic acid levels in the body is essential for maintaining overall health. This highlights the need for ongoing research into its effects and the mechanisms involved.
Biological Functions and Role in the Human Body
Glutamic acid, a non-essential amino acid, plays a vital role in our body. It's one of the building blocks of proteins. This amino acid helps in neurotransmission. It functions as a key player in sending signals in the brain. Therefore, glutamic acid is critical for cognitive functions and mood regulation.
Additionally, it contributes significantly to metabolic processes. Glutamic acid helps in the synthesis of other amino acids. It’s involved in producing energy within the body. When we exercise, this amino acid supports muscle recovery. It rejuvenates our systems by aiding cell function.
**Tip:** Incorporate foods rich in glutamic acid, like spinach and mushrooms, into your diet. This can boost brain health.
Remember, balance is crucial. Too much glutamic acid might lead to imbalances. This can affect mood and cognitive functions. Monitoring intake can help maintain overall well-being.
**Tip:** Keep hydration in check. Water supports nutrient absorption and maintains body balance.
Sources of Glutamic Acid in Diet and Nutrition
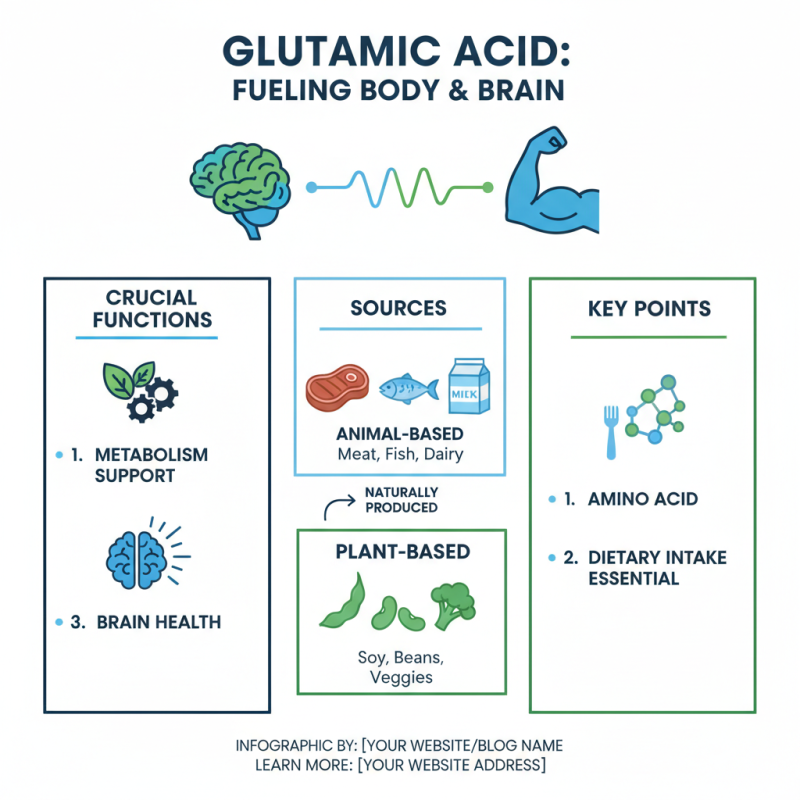
Glutamic acid is an amino acid crucial for many bodily functions. It plays a pivotal role in metabolism and supports brain health. It's produced naturally in the body, but dietary sources are also essential. Foods rich in glutamic acid include meat, fish, and dairy. Plant-based options, such as soy products, beans, and certain vegetables, are also significant sources.
Incorporating glutamic acid into your diet may be easier than you think. Foods like mushrooms and tomatoes are great options. They not only enrich flavors but are nutritious too. However, not everyone consumes enough of these foods. Busy lifestyles can lead to imbalanced diets. Some people might overlook simple, healthy choices.
While many are aware of protein needs, amino acids often get ignored. It’s easy to forget about the importance of glutamic acid. Understanding these dietary elements can encourage better food choices. Reflecting on our daily meals might help us find gaps in nutrition. Are we prioritizing foods rich in glutamic acid?
Health Benefits and Potential Risks of Glutamic Acid
Glutamic acid is a non-essential amino acid. It plays a crucial role in many biological processes. This amino acid is vital for brain function. It helps with neurotransmission and can improve learning and memory. However, there are potential risks to consider.
Some people may react negatively to glutamic acid. For instance, individuals with certain sensitivities might experience headaches or nausea after consumption. Overconsumption of foods high in glutamic acid can lead to an imbalance in neurotransmitter levels. This could impact mood and cognitive function. Listen to your body and recognize your limits.
Tip: Keep a food diary to track your reactions to glutamic acid-rich foods.
Balanced dietary habits can help manage risks. Include a variety of proteins to ensure amino acid diversity. Do not rely solely on glutamic acid for brain health. It is essential to maintain overall nutrition for optimal wellness.
Tip: Try incorporating gentle exercises like yoga to enhance mental clarity. This can reduce the urge to consume excessive glutamate-rich foods due to stress.
Applications of Glutamic Acid in Food and Industry
Glutamic acid plays a significant role in various applications within food and industry. In the food sector, it acts as a flavor enhancer. Many processed foods use glutamic acid to improve savory taste. Research indicates that around 90% of processed foods contain some form of this amino acid. It’s commonly found in broths, sauces, and snack foods. This widespread application raises questions about consumer awareness of its prevalence.
In the industrial realm, glutamic acid has diverse uses. It’s vital in the production of bioplastics and pharmaceuticals. A 2022 report highlighted that 45% of global glutamic acid production is directed towards non-food industries. Its ability to enhance properties in various manufacturing processes is remarkable. However, it’s essential to examine the environmental implications of its large-scale production. Many factories contributing to this figure must improve their sustainability practices.
Glutamic acid's versatility is clear, but the industry must address the potential over-reliance on this compound. Continuous monitoring of its impacts on health and the environment is crucial. The challenge lies in balancing innovation with safety and sustainability. These factors will shape the future of glutamic acid applications.
Related Posts
-

7 Best Ways Glutamic Acid Can Boost Your Health and Wellbeing
-

Navigating the Global Market for Best Glutamic Acid Ultimate Guide to Finding Quality Suppliers
-

5 Key Benefits of Glutamic Acid in Food and Health Industries
-

What is Glutamic Acid Benefits Uses and Sources
-

How to Incorporate Phytic Acid into Your Skincare Routine for Radiant Skin
-

How to Use Azelaic Acid for Clear Skin and Reduced Acne Scars