2026 Best Sodium Phytate Benefits Uses and Health Effects Explained
Sodium Phytate, a naturally occurring compound, has gained attention for its potential health benefits. This unique substance is found in various grains and legumes. Research shows that Sodium Phytate can enhance mineral absorption and promote digestive health. According to the 2022 Nutraceutical Report, incorporating Sodium Phytate in diets may reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Dr. Linda Harper, a renowned expert in nutritional biochemistry, states, "Sodium Phytate demonstrates promise in improving gut health and mineral bioavailability." However, understanding its efficacy requires a careful examination of dosage and individual responses.
Despite the promising benefits, not all findings are conclusive. Some studies suggest that excessive intake may have adverse effects. This calls for further exploration and reflection on Sodium Phytate's role in nutrition. Balancing its use is crucial for harnessing its benefits while avoiding potential downsides.

Overview of Sodium Phytate and Its Chemical Properties
Sodium phytate is a salt derived from phytic acid, found in many plant seeds. It is often recognized for its ability to bind minerals, which can be either beneficial or problematic. The chemical formula for sodium phytate is C6H6NaO24P6, indicating its complex structure. This complexity allows sodium phytate to have various functions in both food and nutritional applications.
One of the interesting aspects of sodium phytate is its ability to chelate minerals. This means it can form complexes with minerals such as calcium, iron, and zinc. Although this is useful in some contexts, it can also lead to nutrient absorption issues. It's a double-edged sword. In whole grains and legumes, sodium phytate may inhibit mineral absorption, raising concerns for those with nutrient deficiencies.
Sodium phytate’s antioxidant properties are noteworthy. They may protect cells from oxidative stress, potentially lowering the risk of chronic diseases. However, the extent of these benefits can vary. Research findings are mixed, sparking debates on its overall health effects. Some studies have shown promise, while others suggest moderation is key. The challenge remains in balancing its advantages with its potential downsides.
2026 Sodium Phytate Health Benefits and Uses
Health Benefits of Sodium Phytate in Nutrition and Wellness
Sodium phytate is gaining attention in nutrition and wellness. It is found naturally in whole grains and legumes. This compound has unique properties that may enhance health.
Research indicates that sodium phytate may have protective effects against oxidative stress. A study published in the "Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry" noted its potential to combat free radicals. This could lead to reduced inflammation and better overall health.
Furthermore, sodium phytate may support mineral absorption. The Bioavailability of essential minerals can sometimes be hindered. However, sodium phytate can help mitigate certain deficiencies. While its impact is notable, the exact benefits can vary widely among individuals. Some may experience improved health, while others might need to reflect on their dietary choices to notice changes.
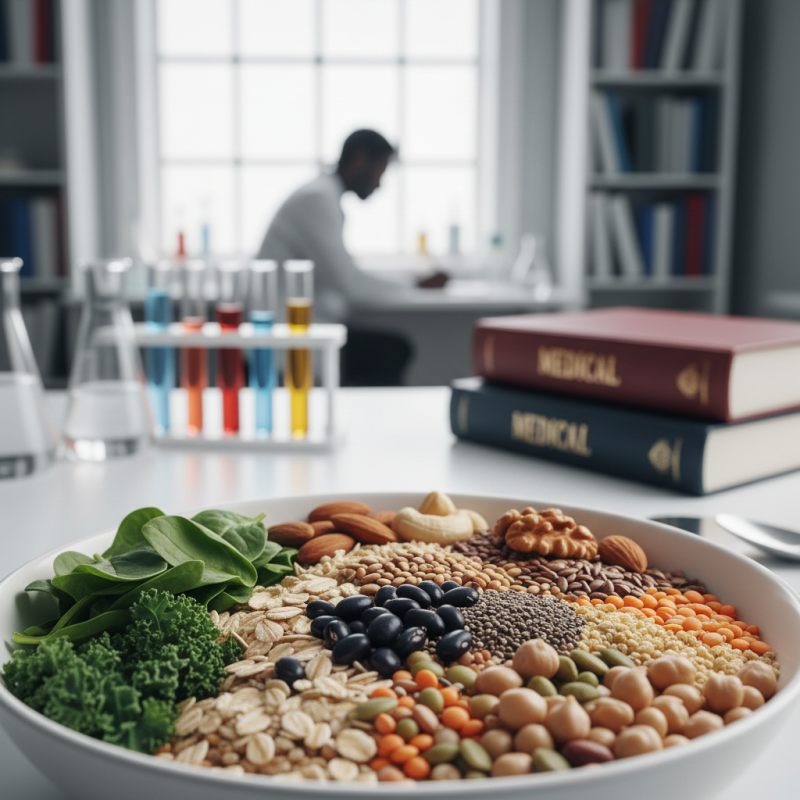
Common Uses of Sodium Phytate in Food and Industry
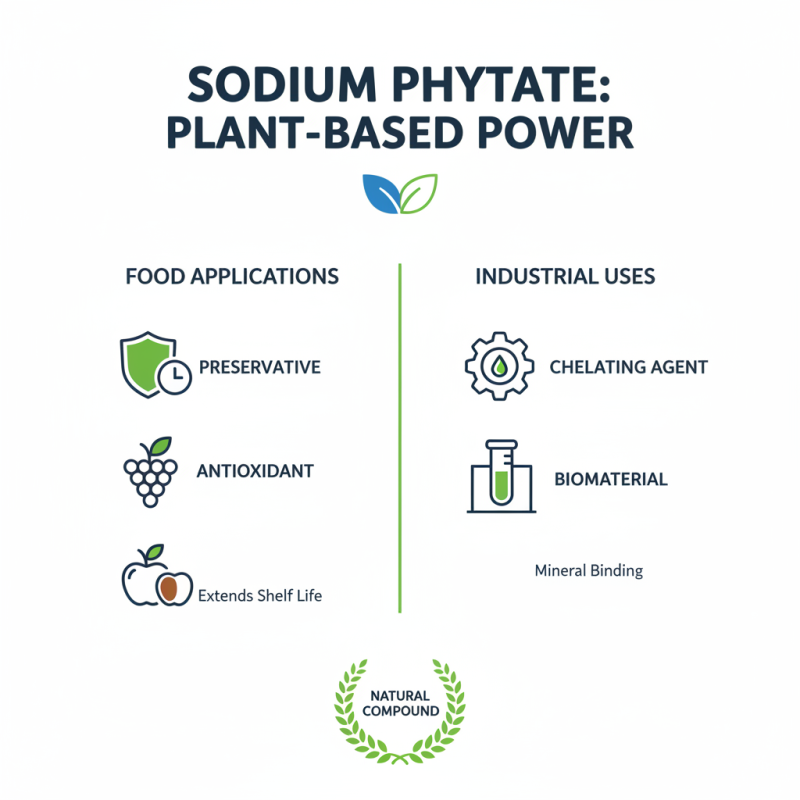
Sodium phytate, a natural compound derived from plants, has various applications in food and industry. It is commonly used as a food additive, mainly as a preservative. It helps to enhance the shelf life of products. Additionally, sodium phytate acts as an antioxidant, protecting foods from oxidative damage.
In the food industry, sodium phytate is often found in baked goods and snack foods. It improves texture and flavor stability. This compound can also bind minerals, potentially affecting their absorption. This interaction is particularly relevant for individuals with specific dietary needs.
**Tip: When consuming foods containing sodium phytate, consider the overall nutritional balance.** If you're relying heavily on fortified foods, monitor your mineral intake.
In the industrial sector, sodium phytate is valued for its chelating properties. It can bind to metal ions, which makes it useful in various applications, including cosmetics and cleaning products. However, it’s essential to weigh the benefits against potential waste generation during manufacturing.
**Tip: Opt for products with clear labeling regarding sodium phytate content.** Understanding ingredient sources can help you make informed choices. This awareness is crucial in minimizing adverse impacts on health and the environment.
Potential Health Effects and Risks of Sodium Phytate Consumption

Sodium phytate, a salt form of phytic acid, is often regarded as a natural antioxidant. It’s rich in minerals like iron and zinc, making it a popular topic in health circles. However, not all effects of sodium phytate are beneficial. Research indicates potential risks associated with its consumption.
While sodium phytate can enhance mineral absorption in some cases, it also binds with minerals, potentially leading to deficiencies. A study published in the Journal of Nutrition noted that sodium phytate can significantly reduce the bioavailability of essential nutrients. This highlights a key concern—imbalanced mineral intake due to excessive consumption of sodium phytate-rich foods can occur. Individuals should be cautious, especially those with existing nutrient deficiencies.
Another concern is its effect on gut health. While it has prebiotic properties that can support gut bacteria, high amounts can lead to gastrointestinal issues. Considerable intake may cause bloating or discomfort. The World Health Organization advises that moderation is crucial. Too much sodium phytate may disrupt nutrient absorption and gut balance, prompting a reconsideration of dietary habits.
Future Research Directions on Sodium Phytate's Applications and Effects
The potential applications of sodium phytate are vast and intriguing. As research continues, new avenues emerge. Studies show that sodium phytate may support mineral absorption. However, results are not always consistent. Some researchers note that it can hinder iron and zinc absorption. This duality poses a unique challenge for nutritionists.
Future research should focus on optimizing sodium phytate's benefits while minimizing drawbacks. This could involve exploring its role in various diets, from vegetarian to omnivorous. Understanding the interaction with different nutrients is crucial. Researchers may investigate varying concentrations and food combinations.
There’s much to explore regarding sodium phytate's health effects. The balance between its inhibitory and beneficial properties remains unclear. Further studies could clarify its impact on chronic diseases. Collaboration between food scientists and nutrition experts might yield promising insights. With careful consideration, sodium phytate could be better utilized in functional foods. The journey is complex, and thoughtful analysis is essential.
2026 Best Sodium Phytate Benefits, Uses and Health Effects Explained
| Benefit/Use | Description | Health Effects | Future Research Directions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antioxidant Properties | Sodium phytate may help neutralize free radicals in the body. | Potential reduction in oxidative stress-related diseases. | Investigating its role in preventing chronic illnesses. |
| Mineral Absorption | Can bind to minerals, affecting their bioavailability. | May lead to deficiencies if intake is excessive. | Understanding optimal intake levels for health. |
| Cholesterol Regulation | May assist in lowering LDL cholesterol levels. | Improved cardiovascular health outcomes. | Clinical studies on long-term effects on cholesterol. |
| Cytoprotective Effects | Protects cells from damage during inflammation. | Potential benefits for conditions like arthritis. | Role in inflammatory response modulation. |
| Gut Health | Can support beneficial gut microbiota. | May improve digestion and nutrient absorption. | Exploring its prebiotic potential. |
Related Posts
-

Exploring Unique Alternatives to the Best Sodium Phytate for Your Needs
-
Exploring Sodium Phytate: Benefits, Uses, and Health Impacts in 2025
-

Understanding the Benefits and Uses of Valaciclovir Hcl for Managing Viral Infections
-

The Ultimate Checklist for Sourcing the Best Valaciclovir Hcl Globally
-

Exploring Methyl Paraben Market Trends at the 138th Canton Fair 2025 in China
-

How to Maximize the Benefits of Levulinic Acid in Biochemical Applications